Creating and Managing Forks#
Tip
For more information see the GitHub documentation
Forks are repositories that share code and visibility settings with the upstream repository. They provide a place for development work to take place while allowing the upstream repo to maintain limited write access. Forks can all merge branches with each other as well as with the upstream repository, meaning a pull request can be opened to merge a branch in a fork into the upstream main.
Creating a Fork#
Creating a fork is something that only needs to be done once per upstream repository. Once created, branches can be created in the fork as desired by the owner.
First navigate to the upstream repository you wish to fork. Then select the fork button.


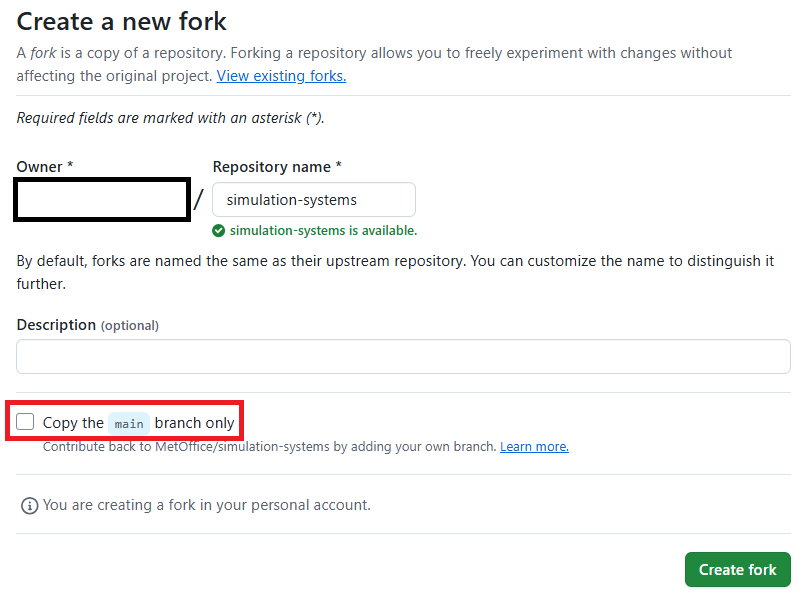
On the next page you can rename your fork if desired and select which branches to fork - ensure this box is unticked to fork all branches.
Important
Ensure the option to only clone the default branch is unticked.
Run the following command, substituting for the required upstream owner and repository name,
gh repo fork <OWNER>/<REPO>
Tip
Add --clone to immediately clone the forked repo
Disable Github Actions in your fork#
It is a good idea to disable GitHub actions on your fork otherwise you will regularly get failures when updating your main branch, due to the failure to deploy documentation. Doing this will not prevent the CI running when you open a pull request.
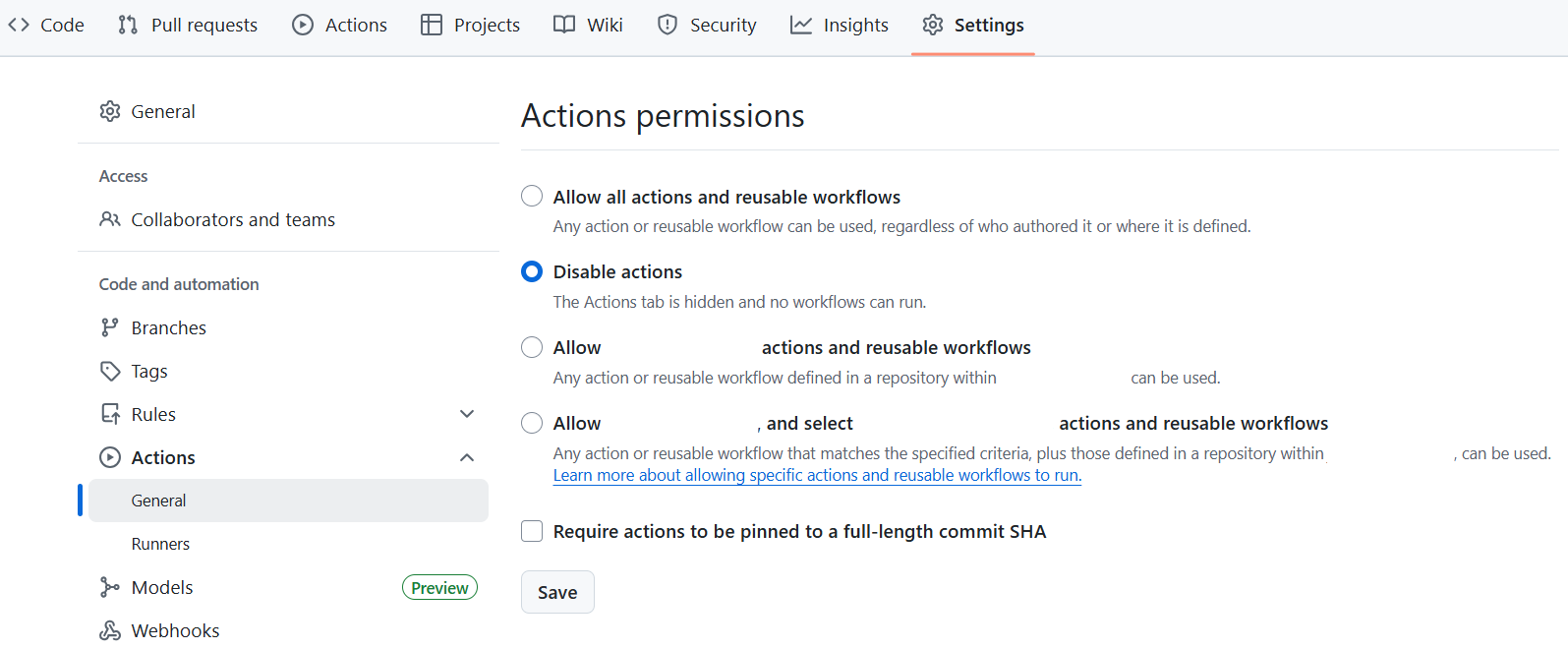
To disable, in your fork on GitHub, navigate to Settings and then
Actions/General. There select the option to Disable actions and save.
Optional - Adding the MetOffice Mirror Bot#
Important
While this step is optional, the suggested approach for extracting code for scientific suites uses these Git Mirrors. If you are likely to use branches in these suites, then this step is recommended.
The mo-gitassist-bot is a user which can be granted read access to a
repository, allowing it to mirror the repository to a central location on
MetOffice platforms. This repository can then be cloned using the local mirror,
avoiding the need to authenticate with GitHub.
This is the recommended approach for extracting code for scientific suites and may be useful for shared accounts which do not have a GitHub account themselves. The mirrors are read only - committing and pushing back to the remote repository will require a GitHub account.
All simulation systems repositories have granted access to this bot, allowing them to be cloned from the mirrors by running,
git clone /path/to/mirrors/MetOffice/repository.git
Please contact the SSD team or the git migration project for the path to the mirrors.
If you wish to be able to access a fork from the mirror, then you will need to
add the bot to your forked repository. First, in your fork, navigate to the
Settings tab and the Collaborators section.
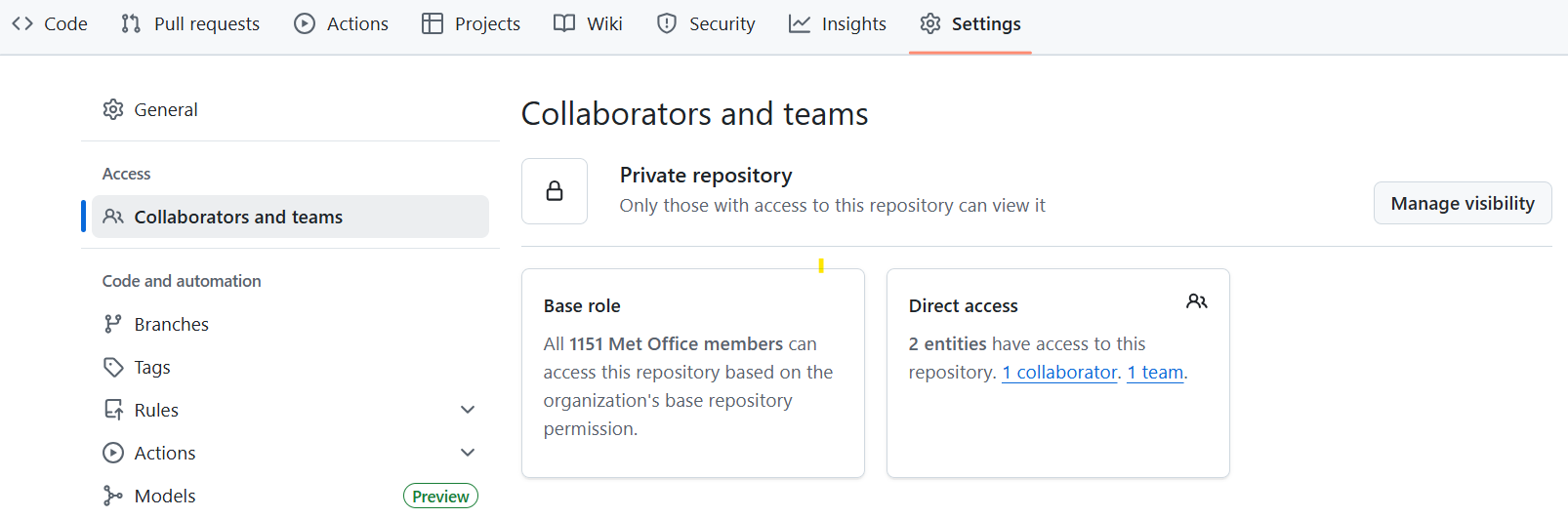
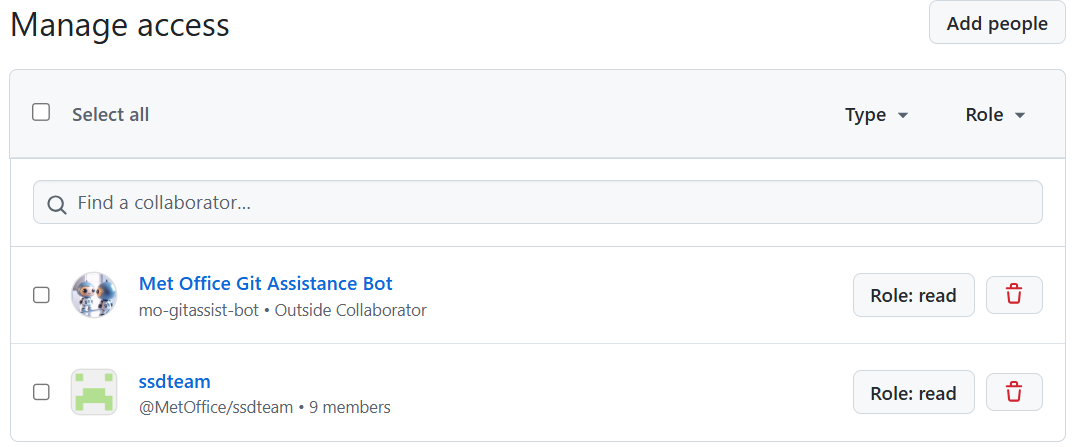
There, use the Add People button to add the mo-gitassist-bot with
Read permissions,
To clone a fork from the mirrors requires a slightly different approach to normally cloning a fork.
# First clone the mirror of the upstream repository
git clone /path/to/mirrors/MetOffice/repository.git && cd repository
# Fetch the fork and branch.
# fork-username is the username of the owner of the desired fork
# fork-branch is the branch to be checked out
git fetch origin <fork-username>/<fork-branch>
# Checkout the forked branch
git checkout FETCH_HEAD
To use the mirrors, you will likely need to run the following once, from the command line:
git config --global --add safe.directory "/path/to/mirrors/MetOffice/*"

